Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems comprise various modules, each addressing a specific business requirement. For example, products-based companies typically have modules for accounting, inventory and order management, customer relationship management (CRM), and if they produce or assemble products, manufacturing. Services businesses may turn to modules for accounting, project management, professional services automation, and CRM.
Why Is ERP Important for Businesses?
ERP systems have become table stakes for businesses looking to use resources wisely. They can help leaders reallocate human and financial capital or build more efficient processes that save money without sacrificing on quality or performance.
An ERP is also an asset when it comes to planning and coordination. Employees can see current available inventory and customer orders in detail, then compare supplier purchase orders and forecasted future demand. If necessary, they can make adjustments to head off problems. ERP software improves communication and collaboration as well because workers can check on the status of other departments to guide their own decisions.
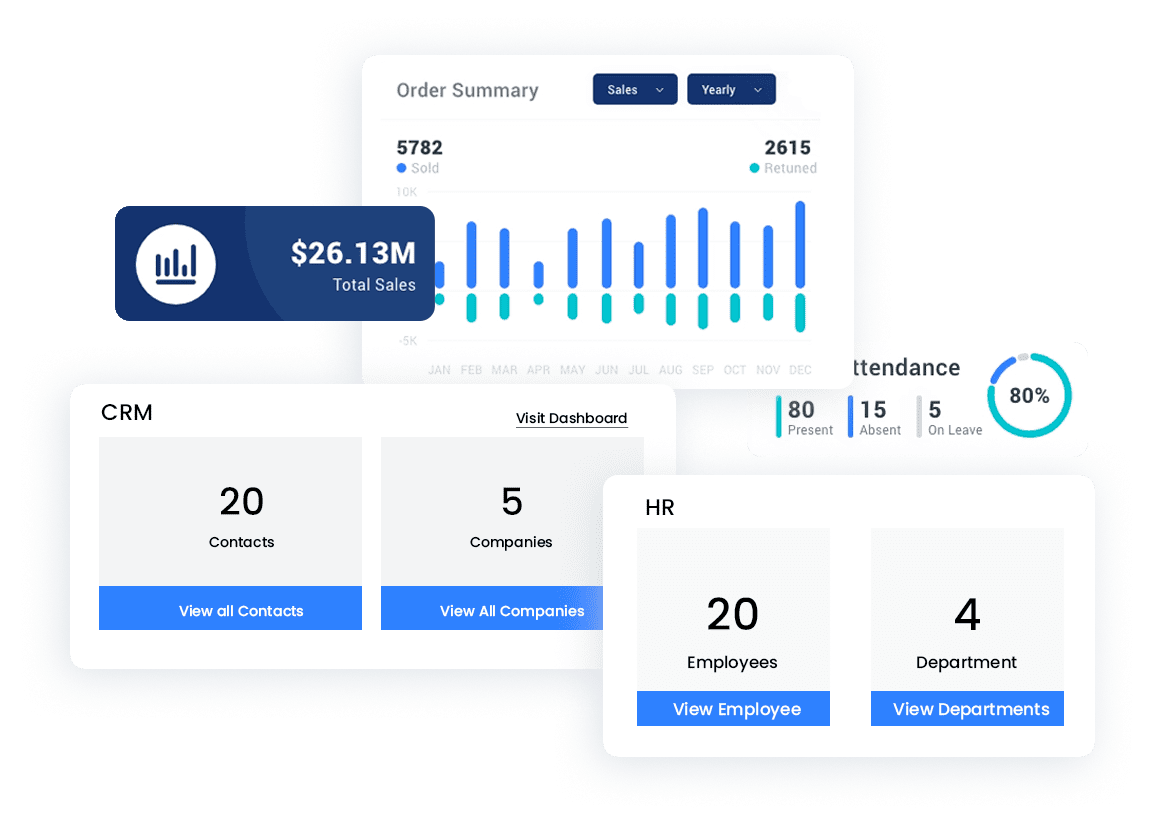
As a comprehensive source of data, an ERP system also provides a host of reports and analytics that can be difference-makers for the business. Turning a vast trove of information into charts and graphs that clearly illustrate trends and help model possible results is an ERP capability executives find invaluable.
How Can ERP Improve or Help a Business?
ERP enables companies to identify areas of the business with room for improvement or opportunities for expansion. User uptake is key: The more employees with access, the more likely teams will spot problems, whether a spike in demand for a certain product, late shipments from a supplier or an impending cash flow crunch. Employees can then proactively mitigate the issue to the extent possible. Executives are generally focused on outcomes — using information to achieve objectives, like increasing efficiency, reducing costs and responding to changing consumer needs or market conditions.
For business units, ERP software can automate many error-prone tasks, like account reconciliations, customer billing and order processing, and provide the information teams need to operate more efficiently. But the real beauty of ERP is that it can give both a 10,000-foot view of the company’s health and detailed insights into a specific process or KPI by not only storing and organising data, but identifying patterns and flagging anomalies that require investigation. Try that with a spreadsheet.
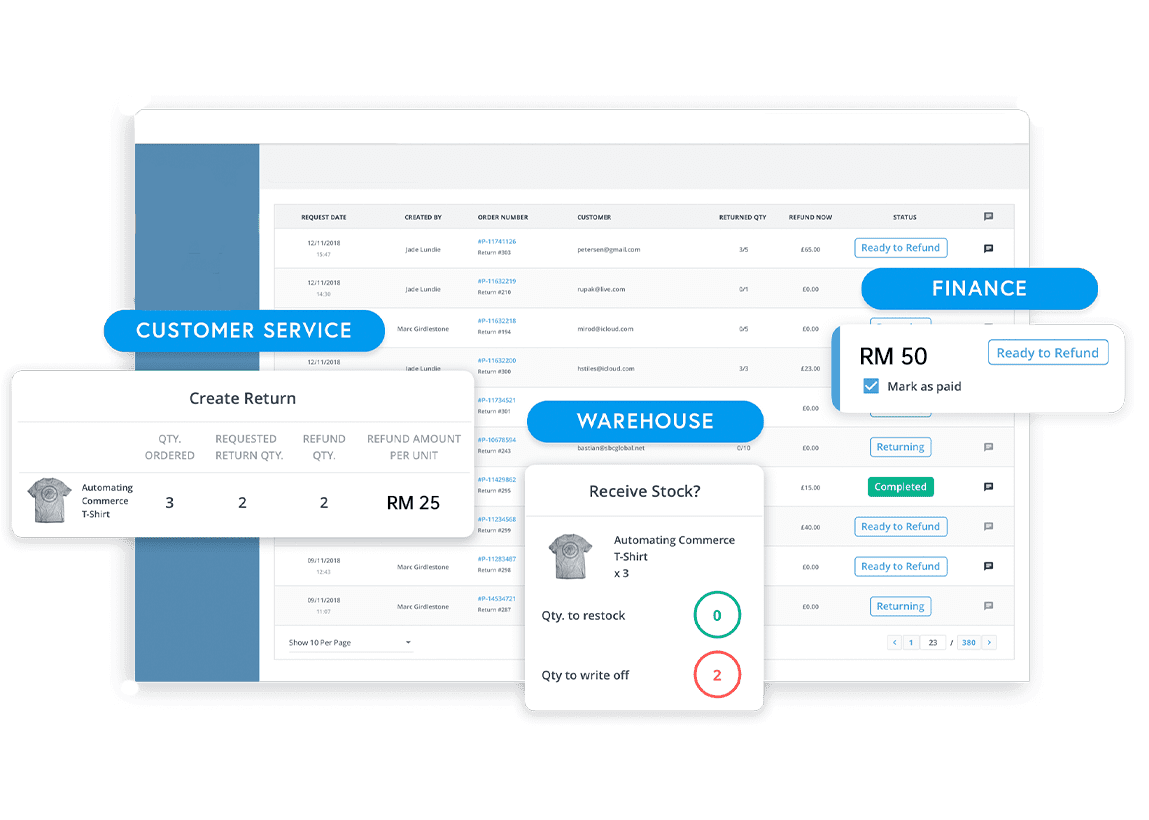
Roles & Users
https://api.whatsapp.com/send?phone=60198811088&text=ERP%20System%20Development Speak Louder with Our Help Today!
Finance/accounting
The accounting team is often the first adopter. This group will track and report on all transactions and other financial information in the system, including accounts payable (AP), accounts receivable (AR) and payroll. With ERP, financial planning and analysis (FP&A) experts — whether a separate role or part of the accounting department — can turn comprehensive financial data into forecasts and reports on revenue, expenses and cash flow.
Supply chain
Employees focused on operations, a group that includes purchasing agents, inventory planners, warehouse managers and senior supply chain leaders, rely on the ERP system to ensure a smooth and continuous flow of goods from supplier to customer. They count on accurate, detailed information provided by the system to optimise inventory levels, prioritise orders, maximise on-time shipments, avoid supply chain disruptions and identify inefficient processes.
Sales and Marketing
An ERP solution can increase the productivity of and drive better results for your sales team by automating lead management and monitoring the interactions prospects have with your company. Reps can document discussions and change the status of prospects as they move through the sales funnel. Using those same records, marketing can automate and manage outreach across all channels, from email to display ads to social media, and measure the effectiveness of those messages and channels to better allocate its budget.
Human resources
The HR department tracks all employee information and broader workforce trends in the ERP. It can quickly find contact information, compensation and benefits details and other documents for each employee. HR can also monitor metrics like retention by department, average pay by title, promotion rate and other metrics to better allocate its own staff and assist line-of-business managers.
ERP Solution
As a rule, ERP business solutions offer the following basic modules

